How To Enable SELinux

 SELinux
SELinux
If you’re using RedHat or CentOS Linux distros (or sporting a Fedora Linux desktop), you probably have SELinux enabled by default. But if it’s been disabled for some reason and you want it back – here’s how you can enable SELinux in your Linux system.
Confirm current SELinux mode
Run the getenforce command to confirm that SELinux is actually disabled:
[root@rhel8 ~]# getenforce
DisabledCheck SElinux status with sestatus
sestatus normally shows verbose SElinux status information, but if SELinux is disabled, you’ll only get one line of output, like this:
root@rhel8 ~]# sestatus
SELinux status: disabled
[root@rhel8 ~]#If sestatus shows that SELinux is disabled, you’ll need to enable it via /etc/selinux.png/config file and reboot the server as shown below.
Permanently Enable SELinux
Do the following two steps to enable SELinux:
- Update /etc/selinux/config file (change SELINUX=disabled to SELINUX=enforcing)
- Reboot your Linux system (shutdown -r now) Once your server comes back online, run sestatus again to make sure SElinux is enabled now:
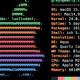
[root@rhel8 ~]# sestatus
SELinux status: enabled
SELinuxfs mount: /sys/fs/selinux.png
SELinux root directory: /etc/selinux.png
Loaded policy name: targeted
Current mode: enforcing
Mode from config file: enforcing
Policy MLS status: enabled
Policy deny_unknown status: allowed
Memory protection checking: actual (secure)
Max kernel policy version: 31