How To Troubleshoot SELinux with Audit Logs

 SELinux
SELinux
I’m post configuring a new RHEL 8 setup on my old PC and want to share some useful SELinux troubleshooting techniques.
How To Check Audit Logs for SELinux
I had a problem with SSH not accepting keys for login. Specifically, I wanted the keys to be in a non-standard /var/ssh/greys/authorized_keys location (instead of my homedir), but SSH daemon would just ignore this file.
I double checked permissions, restarted SSHd and eventually realised that the issue must have been due to SELinux. So I went to inspect the audit logs.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux puts audit logs into /var/log/audit directory. If you’re looking for SELinux issues, just grep for denied – it will show you everything that has recently been blocked:
root@rhel8:~ # grep denied /var/log/audit/*
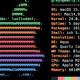
type=AVC msg=audit(1567799177.932:3031): avc: denied { read } for pid=24527 comm="sshd" name="authorized_keys" dev="dm-11" ino=26047253 scontext=system_u:system_r:sshd_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 tcontext=system_u:object_r:var_t:s0 tclass=file permissive=0
type=AVC msg=audit(1567799177.943:3033): avc: denied { read } for pid=24527 comm="sshd" name="authorized_keys" dev="dm-11" ino=26047253 scontext=system_u:system_r:sshd_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 tcontext=system_u:object_r:var_t:s0 tclass=file permissive=0
type=AVC msg=audit(1567799177.956:3035): avc: denied { read } for pid=24527 comm="sshd" name="authorized_keys" dev="dm-11" ino=26047253 scontext=system_u:system_r:sshd_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 tcontext=system_u:object_r:var_t:s0 tclass=file permissive=0I also highlighted the likely problem: SSH daemon is running under sshd_t context, but files in /var/ssh/ directories inherited standard var_t context.
Just to be sure, I checked the context on the default /home/greys/.ssh/authorized_keys file:
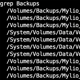
root@rhel8:~ # ls -alZ /home/greys/.ssh/authorized_keys
-rw-------. 1 greys greys unconfined_u:object_r:ssh_home_t:s0 95 Sep 6 20:28 /home/greys/.ssh/authorized_keysThat’s the answer! We need to change /var/ssh/greys/authorized_keys file to the ssh_home_t context.
Updating SELinux context for a file
First, let’s change the SELinux context:
root@rhel8:~ # semanage fcontext -a -t ssh_home_t /var/ssh/greys/authorized_keys… and now we relabel the actual file:
root@rhel8:~ # restorecon -Rv /var/ssh/greys/authorized_keys
Relabeled /var/ssh/greys/authorized_keys from system_u:object_r:var_t:s0 to system_u:object_r:ssh_home_t:s0That’s it – after that my logins using SSH keys started working just fine. Hope you find this example useful!
See Also
- SELinux Reference
- Confirm Current SELinux Mode
- How To Disable SELinux
- How To: List SELinux Contexts for Files
- Where To Learn More About SELinux
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- RHEL8