How To Use watch Command with Quicker Intervals

 watch ifconfig command with 0.2s interval
watch ifconfig command with 0.2s interval
Sometimes you need to monitor a progress of something in your Linux system - how a file size changes or network traffic gets tracked for a particular interface. There are many scenarios where watch command is handy.
Basic watch command usage
Come up with a command that generates the output you want monitored, and pass this command to watch command as parameters.
For instance, if I run ifconfig wlp2s0, it will give me the current state of the WiFi interface on my XPS laptop:
greys@xps:~$ ifconfig wlp2s0
wlp2s0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.xxx.yyy netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.xxx.255
inet6 fe80::af47:a73c:a73c:66b4 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 9c:b6:d0:97:d0:a7 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 562709 bytes 402837160 (384.1 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 1956 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 95351 bytes 15925207 (15.1 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0greys@xps:~$ watch ifconfig -aBy default watch command uses interval of 2sec - meaning it will refresh output every 2 seconds by re-running the same command you specified.
It will look like this:
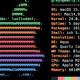
Every 2.0s: ifconfig wlp2s0 xps: Sat Jul 17 20:40:00 2020
wlp2s0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.xxx.yyy netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.xxx.255
inet6 fe80::af47:a73c:a73c:66b4 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 9c:b6:d0:97:d0:a7 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 614256 bytes 435424196 (415.2 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 2142 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 106700 bytes 17857828 (17.0 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0Quicker Intervals for watch command
A friend reminded me the other day, that in Linux it’s actually possible to make watch command wait a lot less between re-runs of the commands you pass to it. You can go as far as making watch re-run every 0.1s, but even 0.2s is going to be 10x better than default - so the counters in my example will now be updating almost instantly.
Just use the -n parameter to specify new time interval:
greys@xps:~$ watch -n0.2 ifconfig wlp2s0Notice how it says Every 0.2s now at the top left corner:
Every 0.2s: ifconfig wlp2s0 xps: Sat Jul 17 20:55:00 2020
wlp2s0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.xxx.yyy netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.xxx.255
inet6 fe80::af47:a73c:a73c:66b4 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 9c:b6:d0:97:d0:a7 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 621467 bytes 437892389 (417.6 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 2156 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 107731 bytes 18036913 (17.2 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0